Tags are used for provisioning, monitoring, and cost control.
All the AWS resources created with Terraform should have tags added that follow a company-wide standard.
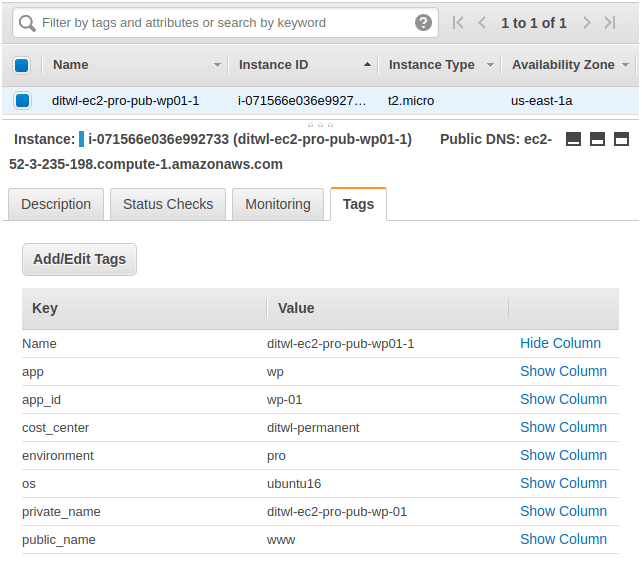
IT Wonder Lab recommended tags:
Values should all be in lowercase without spaces.

IT Wonder Lab tutorials are based on the diverse experience of Javier Ruiz, who founded and bootstrapped a SaaS company in the energy sector. His company, later acquired by a NASDAQ traded company, managed over €2 billion per year of electricity for prominent energy producers across Europe and America. Javier has over 25 years of experience in building and managing IT companies, developing cloud infrastructure, leading cross-functional teams, and transitioning his own company from on-premises, consulting, and custom software development to a successful SaaS model that scaled globally.
Are you looking for cloud automation best practices tailored to your company?