Using the Terraform aws_db_instance resource block to configure, launch, and secure RDS instances.
Welcome to our tutorial series where we dive into cloud infrastructure deployment using Terraform or OpenTofu on AWS. In this series, the fundamentals are shown, guiding you through the process of minimizing resource usage and simplifying the deployment complexities associated with cloud infrastructure. This tutorial series is a work in progress.
This comprehensive OpenTofu and Terraform tutorial guides you step-by-step through creating infrastructure in AWS using Terraform.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) helps maintain consistency, enables version control, enhances collaboration among teams, allows for easier replication of environments, streamlines the deployment and management of infrastructure boosting efficiency, and reducing errors in managing complex systems.
How to start building AWS infrastructure with Terraform: RDS databases
Read previous sections of the tutorial: AWS with Terraform Tutorial
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is a cloud-based service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that simplifies the setup, operation, and scaling of relational databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle, and MariaDB and Amazon Aurora
Definition of RDS Instances with Terraform
Defining RDS Subnet, Security Groups for RDS, AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for RDS credentials, and RDS Instances with Terraform.
Plan, and apply the Terraform plan to select the AWS AMI.
RDS instances have different prices depending on their type, region, and purchase model.
Common Questions About AWS RDS
Can Terraform manage RDS backups and maintenance?, Is it possible to modify existing RDS instances with Terraform? What are the advantages of using Terraform with AWS RDS?
Other tutorials for creating infrastructure in AWS using Terraform
Read previous sections of the tutorial:
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is a cloud-based service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that simplifies the setup, operation, and scaling of relational databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle, and MariaDB and Amazon Aurora. It provides features like automated backups, high availability, and scalability, making it easier for developers to manage their databases without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
RDS instances require an RDS Subnet that includes at least two availabilities zones for redundancy and to enable Multi-AZ deployments and database maintenance operations (upgrades), a security rule, and optionally a KMS Key for RDS credentials.
Security should be taken as a priority when designing any Infrastructure. Databases should be placed in private subnets and have limited exposure through security groups that deny all inbound traffic except the one originating from the back-end server ditwl-ec-back-end-123.
Previous sections of this AWS with Terraform guide have covered basic information about Terraform and AWS and have configured and used the AWS Terraform provider to create a VPC, four subnets, one Internet Gateway, two NAT Gateways, three Routing Tables, Security Groups, and a Private Key.
Add the following blocks to the terraform-aws-tutorial.tf created in previous sections.
An RDS Subnet expanding private subnets: ditwl-sn-za-pro-pri-02 and ditwl-sn-zb-pro-pri-06 providing:
RDS Subnets are created using terraform resource block aws_db_subnet_group.
# Subnet group for the RDS service
resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri" {
name = "ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri"
subnet_ids = [aws_subnet.ditwl-sn-za-pro-pri-02.id, aws_subnet.ditwl-sn-zb-pro-pri-06.id]
}A security group for the RDS Instances. It enables inbound connectivity only from the back-end server ditwl-ec-back-end-123.
Security Groups for RDS are created the same way as for EC2, using terraform resource blocks aws_security_group and aws_security_group_rule.
# Create a Security Group for the RDS Instances
resource "aws_security_group" "ditwl-sg-rds-001" {
name = "ditwl-sg-rds-001"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.ditlw-vpc.id
description = "RDS Instance Security"
}
# Allow access from the back-end to port TCP 3306 (MariaDb)
resource "aws_security_group_rule" "ditwl-sr-back-end-to-db" {
security_group_id = aws_security_group.ditwl-sg-back-end.id
type = "ingress"
from_port = 3306
to_port = 3306
protocol = "tcp"
source_security_group_id = aws_security_group.ditwl-sg-back-end.id
description = "Allow access from the back-end to port TCP 3306 (MariaDb)"
}When using RDS it is possible to delegate to AWS Key Management Service (KMS) the management of the RDS credentials, the KMS will generate a secure random password, will store it in the AWS Secrets Manager, and will rotate it periodically, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
KMS Keys are created using the Terraform resource block aws_kms_key, an alias can be specified to give an easy-to-remember name using the Terraform resource block aws_kms_alias.
# KMS Secrets Manager
resource "aws_kms_key" "ditwl-kms-rds-001-key" {
description = "RDS ditwl-rds-001 Key"
tags = {
"Name" = "ditwl-kms-rds-001-key"
}
}
# KMS Alias
resource "aws_kms_alias" "ditwl-kmsalias-rds-001-key" {
name = "alias/ditwl-kms-rds-001-key"
target_key_id = aws_kms_key.ditwl-kms-rds-001-key.key_id
}RDS Instance/s: ditwl-rds-001
RDS Instances are available for multiple database engines and instance classes. Additionally, it can be configured in Multi-AZ deployment where at least 2 instances are deployed in different availability zones and its data is replicated automatically. Multi-AZ maintains a primary node and a standby instance with automatic database failover in less than 60 seconds, a more advanced configuration enables two read-only standby replicas and a 35-second failover.
RDS Instances are created using the Terraform resource block aws_db_instance.
# RDS (Database)
resource "aws_db_instance" "ditwl-rds-001" {
identifier = "ditwl-rds-001"
engine = "mariadb" //oracle-ee
db_name = "ditwldb01" //The name of the database to create
allocated_storage = 20
instance_class = "db.t4g.micro" //2vCPU 1G Mem (Burstable Graviton2 Processor 64-bit Arm)
db_subnet_group_name = "ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri"
username = "admin"
manage_master_user_password = true
master_user_secret_kms_key_id = aws_kms_key.ditwl-kms-rds-001-key.key_id
skip_final_snapshot = true
backup_retention_period = 0
depends_on = [ aws_db_subnet_group.ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri ]
}Open a command line shell at the same location where the terraform-aws-tutorial.tf file is located, and, run the Terraform or OpenTofu plan, and apply the commands.
Run tofu plan to generate and review the execution plan. Check each line and value to make sure that it corresponds to the desired change.
Terraform will refresh the state by comparing it with the Cloud resources and produce a plan for the resources that need to be created, updated, or destroyed.
In the past section of the tutorial, some resources were commented out to reduce the infrastructure cost during development. The RDS instances have dependencies with some previous resources, please uncomment all resources to proceed with the Terraform plan.
Run the Terraform plan:
$ tofu plan
data.aws_ami.ubuntu-23-04-arm64-minimal: Reading...
...
aws_main_route_table_association.ditwl-rta-default: Refreshing state... [id=rtbassoc-09cc07db0cbfb0a7a]
OpenTofu used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the
following symbols:
+ create
OpenTofu will perform the following actions:
# aws_db_instance.ditwl-rds-001 will be created
+ resource "aws_db_instance" "ditwl-rds-001" {
+ allocated_storage = 20
+ db_name = "ditwldb01"
+ db_subnet_group_name = "ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri"
+ engine = "mariadb"
+ identifier = "ditwl-rds-001"
+ instance_class = "db.t4g.micro"
+ manage_master_user_password = true
...
+ tags_all = {
+ "cost_center" = "marketing-department"
+ "environment" = "pro"
+ "owner" = "IT Wonder Lab"
}
+ timezone = (known after apply)
+ username = "admin"
+ vpc_security_group_ids = (known after apply)
}
# aws_db_subnet_group.ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri will be created
+ resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri" {
+ name = "ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri"
+ subnet_ids = [
+ "subnet-006842d378df0ac09",
+ "subnet-06a52a222034e1007",
]
...
}
# aws_kms_alias.ditwl-kmsalias-rds-001-key will be created
+ resource "aws_kms_alias" "ditwl-kmsalias-rds-001-key" {
+ name = "alias/ditwl-kms-rds-001-key"
}
# aws_kms_key.ditwl-kms-rds-001-key will be created
+ resource "aws_kms_key" "ditwl-kms-rds-001-key" {
+ description = "RDS ditwl-rds-001 Key"
+ tags_all = {
+ "Name" = "ditwl-kms-rds-001-key"
+ "cost_center" = "marketing-department"
+ "environment" = "pro"
+ "owner" = "IT Wonder Lab"
}
}
# aws_security_group.ditwl-sg-rds-001 will be created
+ resource "aws_security_group" "ditwl-sg-rds-001" {
+ arn = (known after apply)
+ description = "RDS Instance Security"
+ name = "ditwl-sg-rds-001"
+ tags_all = {
+ "cost_center" = "marketing-department"
+ "environment" = "pro"
+ "owner" = "IT Wonder Lab"
}
+ vpc_id = "vpc-0b0b93490d844bd26"
}
# aws_security_group_rule.ditwl-sr-back-end-to-db will be created
+ resource "aws_security_group_rule" "ditwl-sr-back-end-to-db" {
+ description = "Allow access from the back-end to port TCP 3306 (MariaDb)"
+ from_port = 3306
+ protocol = "tcp"
+ security_group_id = "sg-08c87b959de8e880f"
+ security_group_rule_id = (known after apply)
+ source_security_group_id = "sg-08c87b959de8e880f"
+ to_port = 3306
+ type = "ingress"
}
Plan: 6 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.Run tofu apply to generate and apply the execution plan. OpenTofu will generate a new plan and ask for confirmation before applying the changes. Review the changes and answer yes or no to apply the changes in AWS.
$ tofu apply
data.aws_ami.ubuntu-23-04-arm64-minimal: Reading...
...
aws_main_route_table_association.ditwl-rta-default: Refreshing state... [id=rtbassoc-09cc07db0cbfb0a7a]
OpenTofu used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the
following symbols:
+ create
OpenTofu will perform the following actions:
# aws_db_instance.ditwl-rds-001 will be created
+ resource "aws_db_instance" "ditwl-rds-001" {
...
}
# aws_db_subnet_group.ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri will be created
+ resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri" {
...
}
# aws_kms_alias.ditwl-kmsalias-rds-001-key will be created
+ resource "aws_kms_alias" "ditwl-kmsalias-rds-001-key" {
...
}
# aws_kms_key.ditwl-kms-rds-001-key will be created
+ resource "aws_kms_key" "ditwl-kms-rds-001-key" {
...
}
# aws_security_group.ditwl-sg-rds-001 will be created
+ resource "aws_security_group" "ditwl-sg-rds-001" {
...
}
# aws_security_group_rule.ditwl-sr-back-end-to-db will be created
+ resource "aws_security_group_rule" "ditwl-sr-back-end-to-db" {
...
}
Plan: 6 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
OpenTofu will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
aws_security_group_rule.ditwl-sr-back-end-to-db: Creating...
aws_kms_key.ditwl-kms-rds-001-key: Creating...
aws_db_subnet_group.ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri: Creating...
aws_security_group.ditwl-sg-rds-001: Creating...
aws_security_group_rule.ditwl-sr-back-end-to-db: Creation complete after 2s [id=sgrule-3481528461]
aws_db_subnet_group.ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri: Creation complete after 3s [id=ditwl-dbsng-zab-pro-pri]
aws_security_group.ditwl-sg-rds-001: Creation complete after 5s [id=sg-0beca4086969e7711]
aws_kms_key.ditwl-kms-rds-001-key: Creation complete after 8s [id=85140d6a-5030-4408-90d0-e8fe73218960]
aws_kms_alias.ditwl-kmsalias-rds-001-key: Creating...
aws_db_instance.ditwl-rds-001: Creating...
aws_kms_alias.ditwl-kmsalias-rds-001-key: Creation complete after 0s [id=alias/ditwl-kms-rds-001-key]
aws_db_instance.ditwl-rds-001: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
...
aws_db_instance.ditwl-rds-001: Still creating... [3m50s elapsed]
aws_db_instance.ditwl-rds-001: Creation complete after 3m52s [id=db-5YYLZZV5SR65HM2GAWM3YRXOQM]
Apply complete! Resources: 6 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyedReview the result, it should be 6 (resource) added, 0 changed, and 0 destroyed.
You can check that the RDS instance has been created in the AWS Console.
Navigate to AWS Console: RDS databases.

Access the RDS admin password using the AWS Console: AWS Secrets Manager: Secrets.
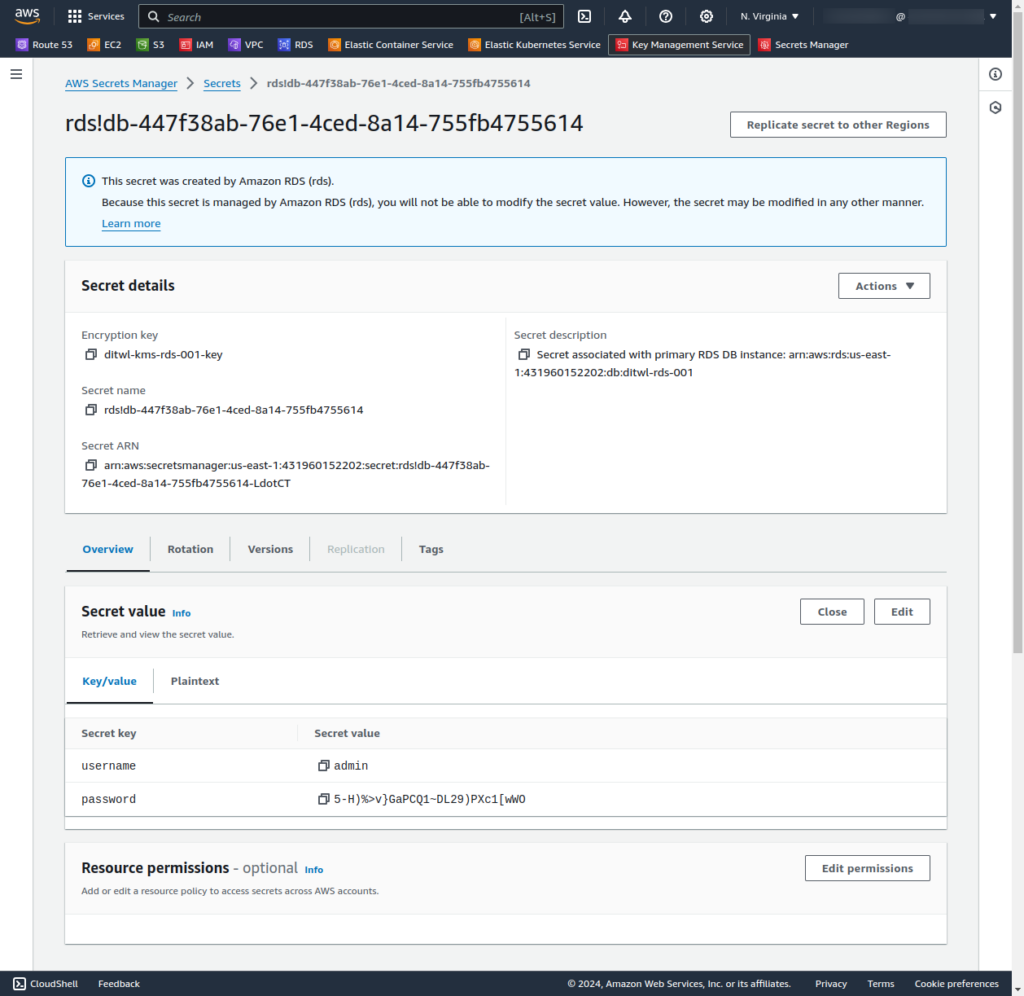
The RDS database instances are located in private subnets that don't give public IP addresses to their instances. Accessing private RDS instances requires a VPN (Site-to-Site VPN, Direct Connect) or using bastion instances. Bastion instances in private subnets can use EC2 Instance Connect if a VPN is unavailable.
AWS will bill the time that the infrastructure is running. To reduce the cost during Terraform development or when the infrastructure is not needed anymore terraform destroy will be used.
Terraform destroy terminates all the resources created by the plan.
Run tofu destroy to generate and apply the destruction plan. OpenTofu will generate a new plan with the resources to terminate and ask for confirmation before applying the changes.
All data will be lost but you will be able to recreate the infrastructure when needed using tofu apply.
$ tofu destroy ... aws_subnet.ditwl-sn-za-pro-pri-02: Destroying... [id=subnet-06a52a222034e1007] aws_kms_key.ditwl-kms-rds-001-key: Destruction complete after 1s aws_subnet.ditwl-sn-za-pro-pri-02: Destruction complete after 2s aws_subnet.ditwl-sn-zb-pro-pri-06: Destruction complete after 2s aws_vpc.ditlw-vpc: Destroying... [id=vpc-0b0b93490d844bd26] aws_vpc.ditlw-vpc: Destruction complete after 3s Destroy complete!
RDS instances have different prices depending on their type, region, purchase model (on-demand, saving plan, or spot), and Multi-AZ configuration. Check Amazon RDS Pricing.
Yes, Terraform can manage RDS backups and maintenance. Automated backups and retention period (backup_retention_period) can be configured using Terraform. A configurable maintenance window controls when maintenance tasks, such as updates and patching, occur on the RDS instances.
Terraform allows you to modify existing RDS instances by updating the corresponding resource blocks in the Terraform configuration file. Some changes require RDS Instance destruction, other parameters can be applied without destroying the databases.
Using Terraform with AWS RDS offers several advantages, including:
This tutorial series is a work in progress and will have these sections:
AWS with Terraform: The Essential Guide: Sections

IT Wonder Lab tutorials are based on the diverse experience of Javier Ruiz, who founded and bootstrapped a SaaS company in the energy sector. His company, later acquired by a NASDAQ traded company, managed over €2 billion per year of electricity for prominent energy producers across Europe and America. Javier has over 25 years of experience in building and managing IT companies, developing cloud infrastructure, leading cross-functional teams, and transitioning his own company from on-premises, consulting, and custom software development to a successful SaaS model that scaled globally.