This tutorial shows how to use Kubernetes Persistent Volumes to store data using an NFS external server. Kubernetes Persistent Volumes (PVs) are storage resources abstracted from the underlying storage details. They allow decoupling storage configuration from pod specifications, providing a way to manage and use storage resources by applications running in Kubernetes clusters.
This tutorial uses an NFS-based Persistent Volumes to store Postgres data directory. The database server (Pod) is deployed as a stateful application (StatefulSet).
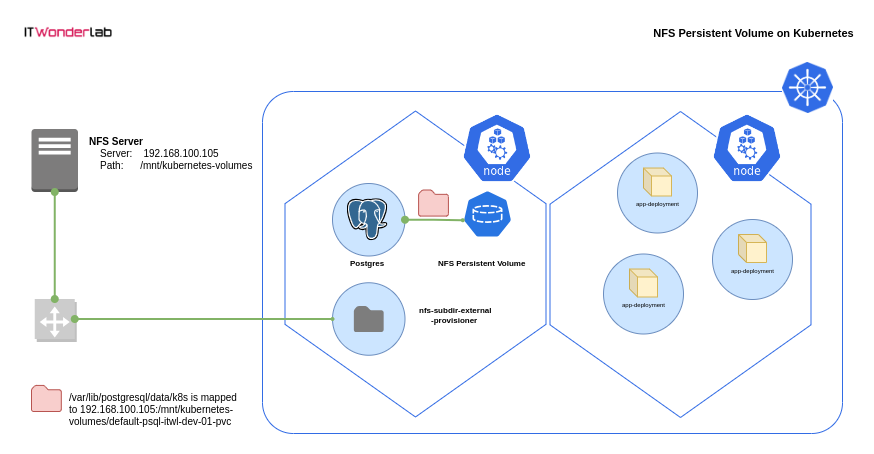
Using Persistent Volumes for Postgres ensures data persistence, scalability, and better management within Kubernetes clusters.
Using NFS (Network File System) in Kubernetes offers a centralized and shared storage solution. It enables multiple pods or nodes to access the same storage volume concurrently, facilitating data sharing and allowing for simpler management of storage across the cluster.
How to run Postgres with a NFS Persistent Volume on Kubernetes
Kubernetes Cluster, Helm, NFS Server.
If you don’t have an existing NFS Server, create a local NFS server.
Install an external NFS provisioner in Kubernetes
Kubernetes doesn't include an internal NFS storage class anymore, an external provisioner needs to be installed.
Deploy Postgres on Kubernetes using an NFS Persistent Volumes
Deploy the needed resources to create a Postgres server on Kubernetes.
Use a Postgres client to connect to the database create a table a insert data.
Debug NFS Subdir External Provisioner on Kubernetes
Debug the different components that provide NFS volumes to Kubernetes
A Kubernetes cluster or install one.
Helm for managing Kubernetes package deployments:
An existing NFS Server and share to store the data
If you don’t have an existing NFS Server, create a local NFS server for the Kubernetes Cluster.
Install the Ubuntu needed packages and create a local directory /mnt/kubernetes-volumes:
sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server sudo mkdir -p /mnt/kubernetes-volumes sudo mkdir -p /mnt/kubernetes-volumes/data sudo chown nobody:nogroup /mnt/kubernetes-volumes/data sudo chmod 777 /mnt/kubernetes-volumes/data
Edit the /etc/exports file to add the exported local directory and limit the share to the CIDR used by the Kubernetes Cluster nodes for external access.
If using the local K3s cluster use your local IP, e.g. 192.168.100.105/32 which corresponds to the network used by the K3s nodes to access the external networks. You can start with * to match and allow all clients and limit later.
Edit /etc/exports and add the NFS share /mnt/kubernetes-volumes configuration:
$ cat /etc/exports # /etc/exports: the access control list for filesystems which may be exported # to NFS clients. See exports(5). # # Example for NFSv2 and NFSv3: # /srv/homes hostname1(rw,sync,no_subtree_check) hostname2(ro,sync,no_subtree_check) # # Example for NFSv4: # /srv/nfs4 gss/krb5i(rw,sync,fsid=0,crossmnt,no_subtree_check) # /srv/nfs4/homes gss/krb5i(rw,sync,no_subtree_check) # /mnt/kubernetes-volumes *(rw,sync,no_subtree_check,insecure,no_root_squash)
Restart the NFS server and verify exported volumes:
# sudo exportfs -a
# sudo systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server
# sudo exportfs -v
/mnt/kubernetes-volumes
<world>(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,rw,insecure,no_root_squash,no_all_squash)
Use the command showmount to list exported shares:
$ showmount -e 192.168.100.105 Export list for 192.168.100.105: /mnt/kubernetes-volumes *
Kubernetes doesn't include an internal NFS provisioner. You need to use an external provisioner to create a StorageClass for NFS.
Check Kubernetes available StorageClasses:
$ kubectl get storageclasses NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE local-path (default) rancher.io/local-path Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 18h
nfs-subdir-external-provisioner will be configured and used to provide NFS storage to PersistentVolumeClaims.
Add the nfs-subdir-external-provisioner repository to Helm and Install the NFS provisioner:
The default installation instructions have been modified to change the naming (pathPattern) of the NFS sub-directories created and preserve directories (onDelete) making it possible to reuse the volumes across Pods restarts.
(add --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml to the helm command if using K3s)
helm repo add nfs-subdir-external-provisioner https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/
$ helm install nfs-subdir-external-provisioner nfs-subdir-external-provisioner/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner \
--set nfs.server=192.168.100.105 \
--set nfs.path=/mnt/kubernetes-volumes \
--set storageClass.onDelete=retain \
--set storageClass.pathPattern='/${.PVC.namespace}-${.PVC.name}' \
--kubeconfig /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml Check that a new nfs-client storage class is available:
$ kubectl get storageclasses NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE local-path (default) rancher.io/local-path Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 19h nfs-client cluster.local/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner Delete Immediate true 15s
Create a Kubernetes resources definition file specifying the Postgres installation, its NFS volume, and a Load Balancer to publish the database server.
The following resources are created:
A Kubernetes StatefulSet ensures stable, unique network identifiers and persistent storage for each pod, making it ideal for applications like databases that require stable hostnames, persistent storage, and ordered deployment/scaling.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: psql-itwl-dev-01-cm
data:
POSTGRES_DB: db
POSTGRES_USER: user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: pass
PGDATA: /var/lib/postgresql/data/k8s
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: nfs-client
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: psql-itwl-dev-01
labels:
app: psql
ver: itwl-dev-01
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: psql
ver: itwl-dev-01
serviceName: "itwl-dev-01"
template: #For the creation of the pod
metadata:
labels:
app: psql
ver: itwl-dev-01
spec:
containers:
- name: postgres
image: postgres:latest
imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
ports:
- containerPort: 5432
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: psql-itwl-dev-01-cm
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data
name: pgdatavol
volumes:
- name: pgdatavol
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: postgres-service-lb
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: psql
ports:
- name: psql
port: 5432
targetPort: 5432
nodePort: 30101
protocol: TCP
Use kubectl to create the resources defined:
kubectl apply -f postgres.yaml
Use the Postgres client psql (sudo apt-get install -y postgresql-client) to connect to the Postgres server, use the Kubernetes cluster IP (e.g. 192.168.100.105) and the LoadBalancer port (e.g. 30101):
Password is pass
$ psql db -h 192.168.100.105 -p 30101 -U user
Password for user user:
psql (14.9 (Ubuntu 14.9-0ubuntu0.22.04.1), server 16.0 (Debian 16.0-1.pgdg120+1))
WARNING: psql major version 14, server major version 16.
Some psql features might not work.
Type "help" for help.
db=#(use \q to exit Postgres client)
CREATE TABLE COLOR(
ID SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
NAME TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
RED SMALLINT NOT NULL,
GREEN SMALLINT NOT NULL,
BLUE SMALLINT NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO COLOR (NAME,RED,GREEN,BLUE) VALUES('GREEN',0,128,0);
INSERT INTO COLOR (NAME,RED,GREEN,BLUE) VALUES('RED',255,0,0);
INSERT INTO COLOR (NAME,RED,GREEN,BLUE) VALUES('BLUE',0,0,255);
INSERT INTO COLOR (NAME,RED,GREEN,BLUE) VALUES('WHITE',255,255,255);
INSERT INTO COLOR (NAME,RED,GREEN,BLUE) VALUES('YELLOW',255,255,0);
INSERT INTO COLOR (NAME,RED,GREEN,BLUE) VALUES('LIME',0,255,0);
INSERT INTO COLOR (NAME,RED,GREEN,BLUE) VALUES('BLACK',255,255,255);
INSERT INTO COLOR (NAME,RED,GREEN,BLUE) VALUES('GRAY',128,128,128);
SELECT * FROM COLOR;
id | name | red | green | blue
----+--------+-----+-------+------
1 | GREEN | 0 | 128 | 0
2 | RED | 255 | 0 | 0
3 | BLUE | 0 | 0 | 255
4 | WHITE | 255 | 255 | 255
5 | YELLOW | 255 | 255 | 0
6 | LIME | 0 | 255 | 0
7 | BLACK | 255 | 255 | 255
8 | GRAY | 128 | 128 | 128
(8 rows)
\qTest Postgress restart and Delete
Test that the Postgres server keeps the data across restarts and even if the deployment is removed and created again.
$ kubectl delete -f postgres.yaml
configmap/psql-itwl-dev-01-cm created
persistentvolumeclaim/psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc created
deployment.apps/psql-itwl-dev-01 created
service/postgres-service-lb created
$ ls -l /mnt/kubernetes-volumes/
total 4
drwxrwxrwx 3 root root 4096 nov 7 20:10 default-psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc
$ kubectl apply -f postgres.yaml
configmap/psql-itwl-dev-01-cm created
persistentvolumeclaim/psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc created
deployment.apps/psql-itwl-dev-01 created
service/postgres-service-lb created
$ psql db -h 192.168.100.105 -p 30101 -U user
Password for user user: pass
psql (14.9 (Ubuntu 14.9-0ubuntu0.22.04.1), server 16.0 (Debian 16.0-1.pgdg120+1))
WARNING: psql major version 14, server major version 16.
Some psql features might not work.
Type "help" for help.
db=# SELECT * FROM COLOR;
id | name | red | green | blue
----+--------+-----+-------+------
1 | GREEN | 0 | 128 | 0
2 | RED | 255 | 0 | 0
3 | BLUE | 0 | 0 | 255
4 | WHITE | 255 | 255 | 255
5 | YELLOW | 255 | 255 | 0
6 | LIME | 0 | 255 | 0
7 | BLACK | 255 | 255 | 255
8 | GRAY | 128 | 128 | 128
(8 rows)
Use kubectl to access Kubernetes logs.
Get the pods and identify the name for the NFS Subdir External Provisioner
$ kubectl get all NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/test-pod 0/1 Completed 0 4h pod/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-55ddd76dc-vk5j9 1/1 Running 1 (32m ago) 119m pod/psql-itwl-dev-01-0 1/1 Running 0 68s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.43.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 23h service/postgres-service-np NodePort 10.43.79.224 <none> 5432:30100/TCP 3h55m service/postgres-service-lb LoadBalancer 10.43.33.127 192.168.100.105 5432:30101/TCP 68s NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner 1/1 1 1 119m NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-55ddd76dc 1 1 1 119m NAME READY AGE statefulset.apps/psql-itwl-dev-01 1/1 68s
Check the pod/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
$ kubectl describe pod/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-55ddd76dc-vk5j9
Name: nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-55ddd76dc-vk5j9
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Service Account: nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
Node: xps13/192.168.100.105
Start Time: Tue, 07 Nov 2023 20:11:26 +0800
Labels: app=nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
pod-template-hash=55ddd76dc
release=nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.42.0.57
IPs:
IP: 10.42.0.57
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-55ddd76dc
Containers:
nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:
Container ID: containerd://66682abf991ea2297ebe0c7019202dd086b9dca352acf987ac2cbf695e10f63b
Image: registry.k8s.io/sig-storage/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2
Image ID: registry.k8s.io/sig-storage/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner@sha256:63d5e04551ec8b5aae83b6f35938ca5ddc50a88d85492d9731810c31591fa4c9
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Tue, 07 Nov 2023 21:38:39 +0800
Last State: Terminated
Reason: Error
Exit Code: 255
Started: Tue, 07 Nov 2023 20:11:27 +0800
Finished: Tue, 07 Nov 2023 21:38:38 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 1
Environment:
PROVISIONER_NAME: cluster.local/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
NFS_SERVER: 192.168.100.105
NFS_PATH: /mnt/kubernetes-volumes
Mounts:
/persistentvolumes from nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-root (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-ntzfj (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-root:
Type: NFS (an NFS mount that lasts the lifetime of a pod)
Server: 192.168.100.105
Path: /mnt/kubernetes-volumes
ReadOnly: false
kube-api-access-ntzfj:
Type: Projected (a volume that contains injected data from multiple sources)
TokenExpirationSeconds: 3607
ConfigMapName: kube-root-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional: <nil>
DownwardAPI: true
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Pulled 33m (x2 over 121m) kubelet Container image "registry.k8s.io/sig-storage/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2" already present on machine
Normal Created 33m (x2 over 121m) kubelet Created container nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
Normal Started 33m (x2 over 121m) kubelet Started container nfs-subdir-external-provisionerIdentify the list of PersistentVolumeClaims (PVC)
$ kubectl get PersistentVolumeClaim NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE test-claim Bound pvc-cdb6bc6a-47a2-4003-8b4b-b60a66d83d94 1Mi RWX nfs-client 115m psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc Bound pvc-73536ecd-7a33-4b5e-9449-65416f1ec26d 1Gi RWX nfs-client 2m18s
Access the log of the PersistentVolumeClaim
$ kubectl describe PersistentVolumeClaim/psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc
Name: psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc
Namespace: default
StorageClass: nfs-client
Status: Bound
Volume: pvc-73536ecd-7a33-4b5e-9449-65416f1ec26d
Labels: <none>
Annotations: nfs.io/storage-path: psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc
pv.kubernetes.io/bind-completed: yes
pv.kubernetes.io/bound-by-controller: yes
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-provisioner: cluster.local/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
volume.kubernetes.io/storage-provisioner: cluster.local/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
Finalizers: [kubernetes.io/pvc-protection]
Capacity: 1Gi
Access Modes: RWX
VolumeMode: Filesystem
Used By: psql-itwl-dev-01-9d8d4b8d5-vxcg2
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ExternalProvisioning 104s (x3 over 111s) persistentvolume-controller waiting for a volume to be created, either by external provisioner "cluster.local/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner" or manually created by system administrator
Normal Provisioning 103s cluster.local/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner_nfs-subdir-external-provisioner-55ddd76dc-9j7kh_6e3d5fde-4cd1-4c66-aaf0-7a256b2e1d9c External provisioner is provisioning volume for claim "default/psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc"
Normal ProvisioningSucceeded 102s cluster.local/nfs-subdiReview the log of the Application using the PersistentVolumeClaim, in this example Postgres
$ kubectl describe pod/psql-itwl-dev-01-0
Name: psql-itwl-dev-01-0
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Service Account: default
Node: xps13/192.168.100.105
Start Time: Tue, 07 Nov 2023 22:10:05 +0800
Labels: app=psql
controller-revision-hash=psql-itwl-dev-01-6bb947769c
statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name=psql-itwl-dev-01-0
ver=itwl-dev-01
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.42.0.65
IPs:
IP: 10.42.0.65
Controlled By: StatefulSet/psql-itwl-dev-01
Containers:
postgres:
Container ID: containerd://edb90feae561895d3d37efcc86dbddef293ebb963cf25e57a229229bd5ac2260
Image: postgres:latest
Image ID: docker.io/library/postgres@sha256:a80d0c1b119cf3d6bab27f72782f16e47ab8534ced937fa813ec2ab26e1fd81e
Port: 5432/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Tue, 07 Nov 2023 22:10:06 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment Variables from:
psql-itwl-dev-01-cm ConfigMap Optional: false
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/lib/postgresql/data from pgdatavol (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-f8j9r (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
pgdatavol:
Type: PersistentVolumeClaim (a reference to a PersistentVolumeClaim in the same namespace)
ClaimName: psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc
ReadOnly: false
kube-api-access-f8j9r:
Type: Projected (a volume that contains injected data from multiple sources)
TokenExpirationSeconds: 3607
ConfigMapName: kube-root-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional: <nil>
DownwardAPI: true
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning FailedScheduling 3m31s default-scheduler 0/1 nodes are available: pod has unbound immediate PersistentVolumeClaims. preemption: 0/1 nodes are available: 1 Preemption is not helpful for scheduling..
Normal Scheduled 3m29s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/psql-itwl-dev-01-0 to xps13
Normal Pulled 3m29s kubelet Container image "postgres:latest" already present on machine
Normal Created 3m29s kubelet Created container postgres
Normal Started 3m29s kubelet Started container postgresCheck the NFS root directory on the NFS server
$ ls -l /mnt/kubernetes-volumes/ total 4 drwxrwxrwx 3 root root 4096 nov 7 20:04 default-psql-itwl-dev-01-pvc
Delete the resources and start again
If you want to delete the resources and start again, use these commands:
helm delete nfs-subdir-external-provisioner --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml kubectl delete -f postgres.yaml

IT Wonder Lab tutorials are based on the diverse experience of Javier Ruiz, who founded and bootstrapped a SaaS company in the energy sector. His company, later acquired by a NASDAQ traded company, managed over €2 billion per year of electricity for prominent energy producers across Europe and America. Javier has over 25 years of experience in building and managing IT companies, developing cloud infrastructure, leading cross-functional teams, and transitioning his own company from on-premises, consulting, and custom software development to a successful SaaS model that scaled globally.
Are you looking for cloud automation best practices tailored to your company?