K3s.io is a Lightweight Kubernetes cluster perfect for development or edge deployments. K3s is a CNCF Sandbox Project Originally developed by Rancher.
How to install K3s a Lightweight Kubernetes for local development
Download and run the installation script.
Check that the Kubernetes cluster is running and the name of the context.
Kube config permissions: Change permissions so other programs can access the configuration.
Deploy a Kubernetes container.
To install follow the official installation instructions or run the quick-start script.
Check the script content for security before running it!
Allow no root users to access the Kubernetes file.
The INSTALL_K3S_EXEC environment variable is included with the parameter --write-kubeconfig-mode=644 to set the kubeconfig file /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml group and world-readable.
See K3s Configuration Options for advanced command line installation options.
$ sudo curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | INSTALL_K3S_EXEC="server --write-kubeconfig-mode=644" sh - [sudo] password for user: [INFO] Finding release for channel stable [INFO] Using v1.27.7+k3s2 as release [INFO] Downloading hash https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases/download/v1.27.7+k3s2/sha256sum-amd64.txt [INFO] Downloading binary https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases/download/v1.27.7+k3s2/k3s [INFO] Verifying binary download [INFO] Installing k3s to /usr/local/bin/k3s [INFO] Skipping installation of SELinux RPM [INFO] Skipping /usr/local/bin/kubectl symlink to k3s, already exists [INFO] Skipping /usr/local/bin/crictl symlink to k3s, already exists [INFO] Skipping /usr/local/bin/ctr symlink to k3s, command exists in PATH at /usr/bin/ctr [INFO] Creating killall script /usr/local/bin/k3s-killall.sh [INFO] Creating uninstall script /usr/local/bin/k3s-uninstall.sh [INFO] env: Creating environment file /etc/systemd/system/k3s.service.env [INFO] systemd: Creating service file /etc/systemd/system/k3s.service [INFO] systemd: Enabling k3s unit Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/k3s.service → /etc/systemd/system/k3s.service. [INFO] systemd: Starting k3s
Check that the Kubernetes cluster is running by requesting information about the nodes:
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION xps13 Ready control-plane,master 15d v1.27.7+k3s2
A kubeconfig is a configuration file used by kubectl, the command-line tool for interacting with Kubernetes clusters. This file stores information about clusters, authentication details, context, and other settings needed to communicate with a Kubernetes cluster. It specifies the cluster's API server, authentication methods (such as certificates or tokens), and the default namespace for operations. The kubeconfig file allows users to manage multiple clusters and switch between them easily using kubectl.
Check the name of the Kubernetes context by requesting information about the kubeconfig file:
$ kubectl config view
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: DATA+OMITTED
server: https://127.0.0.1:6443
name: default
contexts:
- context:
cluster: default
user: default
name: default
current-context: default
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: default
user:
client-certificate-data: DATA+OMITTED
client-key-data: DATA+OMITTEDIn this example the Kubernetes cluster name is default.
Different applications like OpenTofu, Terraform, or the VS Code Kubernetes extension that run without sudo need access to the kubeconfig file.
WARN[0000] Unable to read /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml, please start server with --write-kubeconfig-mode to modify kube config permissions.
Options:
$ sudo chmod 644 /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yamlFor adding or modifying clusters in the Kubeconfig, use a root user or prefix the kubectl config command with sudo, example:
$ sudo kubectl config set-cluster ditwl-eks-01 --server=https://EA21C5BB81C481ED63221F7D963D.gr7.us-east-1.eks.am azonaws.com Cluster "ditwl-eks-01" set.
OpenTofu and Terraform, or the VS Code Kubernetes extension expect Kubeconfig file to be at the default location $HOME/. kube/config but K3s uses a different location.
For OpenTofu and Terraform set the path in the Provider:
provider "kubernetes" {
#kubeconfig file, if using K3S set the path
config_path = "/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml"
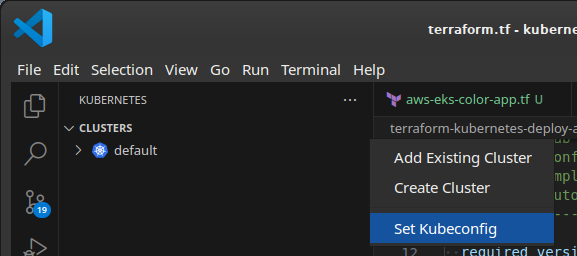
}For VS Code Kubernetes extension, manually select the location of Kubeconfig using the extension menu (click on ...)

IT Wonder Lab tutorials are based on the diverse experience of Javier Ruiz, who founded and bootstrapped a SaaS company in the energy sector. His company, later acquired by a NASDAQ traded company, managed over €2 billion per year of electricity for prominent energy producers across Europe and America. Javier has over 25 years of experience in building and managing IT companies, developing cloud infrastructure, leading cross-functional teams, and transitioning his own company from on-premises, consulting, and custom software development to a successful SaaS model that scaled globally.