Accessing applications deployed in a Kubernetes Cluster using VirtualBox requires a NodePort. In a cloud provider, a load balancer will be used.
Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on top of VirtualBox requires a specific network configuration as seen in the Kubernetes Cluster using Vagrant and Ansible and First Steps After Kubernetes Installation tutorials.
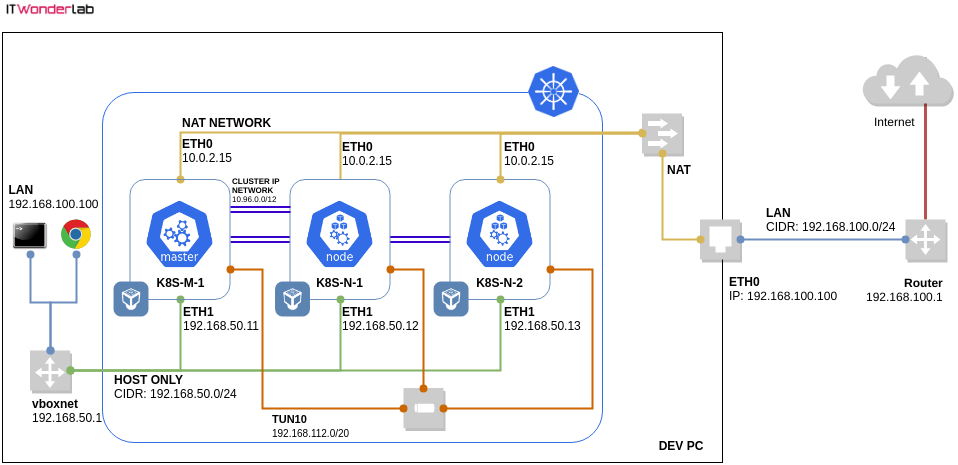
The tutorial shows how to deploy an application and a NodePort to publish the application outside the Kubernetes Cluster.
Prerequisites:
Create an Application configuration file that defines the name of the application, labels, number of replicas, and the docker images that are needed. Save the file as nginx.yaml.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: my-echo
image: gcr.io/google_containers/echoserver:1.8Apply the configuration to the Kubernetes Cluster
$ kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml deployment.apps/nginx-deployment created
The Docker image, in this example nginx, has to be available in the official public Docker Registry (if using a local Docker image, it first needs to be uploaded to the public registry or a private registry, see Pull an Image from a Private Registry or the section Building the Color Application in the Istio Patterns: Traffic Splitting in Kubernetes (Canary Release) tutorial).
In order to access the echo server that we just deployed from outside the cluster a NodePort needs to be created, the NodePort will allow us to access each of the Nginx echo servers (in round-robin) from outside the cluster.
In a Kubernetes cluster hosted in a cloud provider like Azure, Google or AWS a cloud-native Load Balancer will be used instead of the NodePort.
Add the following definition to nginx.yaml (the file created before)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service-np
labels:
name: nginx-service-np
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8082 # Cluster IP, i.e. http://10.103.75.9:8082
targetPort: 8080 # Application port
nodePort: 30000 # (EXTERNAL-IP VirtualBox IPs) i.e. http://192.168.50.11:30000/ http://192.168.50.12:30000/ http://192.168.50.13:30000/
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app: nginx
Apply the configuration to the Kubernetes Cluster
$ kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml deployment.apps/nginx-deployment unchanged service/nginx-service-np created
Check to see if the NodePort hast been created
$ kubectl get services NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 7h55m nginx-service-np NodePort 10.103.75.9 <none> 8082:30000/TCP 5h43m
Access the application with curl (or with a web browser) from the development environment using one of the public Kubernetes Cluster IPs (192.168.50.11, 192.168.50.12, 192.168.50.13) and the NodePort (30000):
$ curl http://192.168.50.11:30000/ Hostname: nginx-deployment-d7b95894f-2hpjk Pod Information: -no pod information available- Server values: server_version=nginx: 1.13.3 - lua: 10008 Request Information: client_address=192.168.116.0 method=GET real path=/ query= request_version=1.1 request_uri=http://192.168.50.11:8080/ Request Headers: accept=*/* host=192.168.50.11:30000 user-agent=curl/7.61.0 Request Body: -no body in request-
Repeat the request and see that the value of hostname changes as Kubernetes is accessing the different instances of the application among the available PODS. The hostname corresponds to the NAME of the different PODS for the Nginx deployment:
$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-deployment-d7b95894f-2hpjk 1/1 Running 1 5h44m nginx-deployment-d7b95894f-49lrh 1/1 Running 1 5h44m nginx-deployment-d7b95894f-wl497 1/1 Running 1 5h44m
The diagram shows the different elements that are involved in publishing an application outside the Kubernetes cluster using a NodePort. The Kubernetes master, not shown, executes a proxy as well.
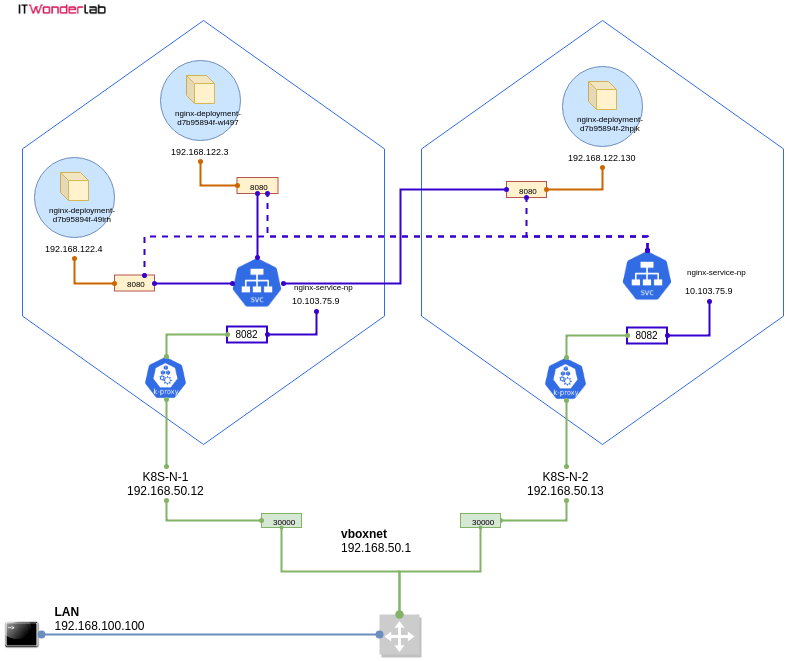
Network traffic when doing curl http://192.168.50.12:30000/

IT Wonder Lab tutorials are based on the diverse experience of Javier Ruiz, who founded and bootstrapped a SaaS company in the energy sector. His company, later acquired by a NASDAQ traded company, managed over €2 billion per year of electricity for prominent energy producers across Europe and America. Javier has over 25 years of experience in building and managing IT companies, developing cloud infrastructure, leading cross-functional teams, and transitioning his own company from on-premises, consulting, and custom software development to a successful SaaS model that scaled globally.
running headless can access nginx app on local workstation, can you tell me easiest way to access from remote workstation / internet
Excelente amigo, me fue de gran ayuda.
Gracias!
Congratulations on a wonderful piece of work.
It saved me several hours of work and I have moved away from spending hours trying out different stuff to working on real life stuff that matters.
Regards
Rama