After installing a Kubernetes Cluster it is recommended to:
This tutorial is a continuation of Kubernetes Cluster using Vagrant and Ansible.
Prerequisites:
We will use vagrant ssh command to access the Kubernetes servers.
jruiz@XPS13:~/git/github/ansible-vbox-vagrant-kubernetes$ vagrant ssh k8s-m-1 Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-31-generic x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage System information as of Fri 31 Jul 2020 05:50:30 PM UTC System load: 0.4 Users logged in: 0 Usage of /: 6.1% of 61.31GB IPv4 address for docker0: 172.17.0.1 Memory usage: 44% IPv4 address for eth0: 10.0.2.15 Swap usage: 0% IPv4 address for eth1: 192.168.50.11 Processes: 163 IPv4 address for tunl0: 192.168.116.0 95 updates can be installed immediately. 36 of these updates are security updates. To see these additional updates run: apt list --upgradable This system is built by the Bento project by Chef Software More information can be found at https://github.com/chef/bento Last login: Fri Jul 31 17:46:30 2020 from 10.0.2.2 vagrant@k8s-m-1:~$
Open a Vagrant SSH to k8s-m-1 and check syslog file for errors
jruiz@XPS13:~/git/github/ansible-vbox-vagrant-kubernetes$ vagrant ssh k8s-m-1 Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-31-generic x86_64) ... vagrant@k8s-m-1:~$ tail -f /var/log/syslog Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Listening on GnuPG cryptographic agent and passphrase cache (restricted). Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Reached target Paths. Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Reached target Timers. Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Listening on GnuPG cryptographic agent and passphrase cache. Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Listening on GnuPG cryptographic agent (ssh-agent emulation). Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Reached target Sockets. Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Reached target Basic System. Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Reached target Default. Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[1]: Started User Manager for UID 1000. Apr 20 14:32:05 k8s-m-1 systemd[7025]: Startup finished in 29ms. ^C
Open a Vagrant SSH to k8s-m-1 and execute kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
jruiz@XPS13:~/git/github/ansible-vbox-vagrant-kubernetes$ vagrant ssh k8s-m-1 Welcome to Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-31-generic x86_64) ... vagrant@k8s-m-1:~$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE default nginx-deployment-6dd86d77d-l9dd9 1/1 Running 1 19h default nginx-deployment-6dd86d77d-qr6dl 1/1 Running 1 19h kube-system calico-kube-controllers-5cbcccc885-pwgmg 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system calico-node-2cj4q 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system calico-node-q25j7 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system calico-node-vkbj5 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system coredns-fb8b8dccf-nfs4w 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system coredns-fb8b8dccf-tmrcg 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system etcd-k8s-m-1 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system kube-apiserver-k8s-m-1 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system kube-controller-manager-k8s-m-1 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system kube-proxy-jxfjf 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system kube-proxy-ljr26 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system kube-proxy-mdgmb 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system kube-scheduler-k8s-m-1 1/1 Running 2 21h kube-system kubernetes-dashboard-5f7b999d65-l8bsx 1/1 Running 1 19h
Install kubectl to administer the Kubernetes Cluster from your development host
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add - echo "deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y kubectl
Copy the Kubernetes config to your local home .kube dir
#Create the configuration directory
$ mkdir -p ~/.kube
#Find the SSH port of the k8s-m-1 server
$ vagrant port k8s-m-1
The forwarded ports for the machine are listed below. Please note that
these values may differ from values configured in the Vagrantfile if the
provider supports automatic port collision detection and resolution.
22 (guest) => 2222 (host)
#Copy the file using scp (ssh password is vagrant)
$ scp -P 2222 [email protected]:/home/vagrant/.kube/config ~/.kube/config
[email protected]'s password: vagrant
config 100% 5449 118.7KB/s 00:00
List the Kubernetes cluster nodes using kubectl from your development host:
$ kubectl cluster-info Kubernetes master is running at https://192.168.50.11:6443 KubeDNS is running at https://192.168.50.11:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'. $ kubectl get nodes --all-namespaces NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-m-1 Ready master 12m v1.18.6 k8s-n-1 Ready <none> 10m v1.18.6 k8s-n-2 Ready <none> 7m43s v1.18.6 $ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kube-system calico-kube-controllers-578894d4cd-nf4pm 1/1 Running 0 12m kube-system calico-node-8pv65 1/1 Running 0 8m2s kube-system calico-node-nmqmr 1/1 Running 0 12m kube-system calico-node-zcdd4 1/1 Running 0 10m kube-system coredns-66bff467f8-6jnkg 1/1 Running 0 12m kube-system coredns-66bff467f8-qs54m 1/1 Running 0 12m kube-system etcd-k8s-m-1 1/1 Running 0 12m kube-system kube-apiserver-k8s-m-1 1/1 Running 0 12m kube-system kube-controller-manager-k8s-m-1 1/1 Running 0 12m kube-system kube-proxy-j8gwm 1/1 Running 0 10m kube-system kube-proxy-jxww4 1/1 Running 0 12m kube-system kube-proxy-lvkd2 1/1 Running 0 8m2s kube-system kube-scheduler-k8s-m-1 1/1 Running 0 12m kubernetes-dashboard dashboard-metrics-scraper-6b4884c9d5-ttqtt 1/1 Running 0 4m24s kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard-7b544877d5-5hjr6 1/1 Running 0 4m24s
The Kubernetes Dashboard provides a web-based user interface to deploy applications, troubleshoot and manage resources. The same functionality is provided through the command line tools but under a very nice web application with charts and beautiful screens.
To deploy the Web UI (Dashboard) or Kubernetes Dashboard run the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.0.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
The deployment file will publish the Kubernetes Dashboard using a ClusterIP service as shown below using TargetPort 8443:
$ kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard describe service kubernetes-dashboard
Name: kubernetes-dashboard
Namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
Labels: k8s-app=kubernetes-dashboard
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"k8s-app":"kubernetes-dashboard"},"name":"kubernetes-dashboard"...
Selector: k8s-app=kubernetes-dashboard
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.98.98.132
Port: <unset> 443/TCP
TargetPort: 8443/TCP
Endpoints: 192.168.122.134:8443
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>To access the Kubernetes Dashboard from our workstation, a NodePort will be created to publish the kubernetes-dashboard following the Publish an Application Outside Kubernetes Cluster instructions.
The file kubernetes-dashboard-service-np.yaml (included in the Kubernetes Cluster using Vagrant and Ansible tutorial source code):
kubernetes-dashboard-service-np.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard-service-np
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8443
nodePort: 30002
targetPort: 8443
protocol: TCP
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
Apply the changes
$ kubectl apply -f kubernetes-dashboard-service-np.yaml serviceaccount/admin-user created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/admin-user created service/kubernetes-dashboard-service-np created
Obtain an authentication token to use on the Kubernetes Dashboard authentication realm
$ kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard describe secret $(kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get secret | grep admin-user | awk '{print $1}')
Name: admin-user-token-f9zj6
Namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: admin-user
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: 29edd185-e261-44e0-ac15-f73d4fccd4fa
Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
ca.crt: 1025 bytes
namespace: 20 bytes
token: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Ikg0c21nUjZ5Rm00cktvRmdMR0FsRXZicVdyYWZvNkQ0MDQ2ck1IV3ZWeHcifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLWRhc2hib2FyZCIsImt1Vybdadas2ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VjcmV0Lm5hbWUiOiJhZG1pbi11c2VyLXRva2VuLWY5emo2Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9zZXJ2aWNlLWFjY291bnQubmFtZSI6ImFkbWluLXVzZXIiLCJrdWJlcm5ldGVfaslvL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50L3NlcnZpY2UtYWNjb3VudC51aWQiOiIyOWVkZDE4NS1lMjYxLTQ0ZTAtYWMxNS1mNzNkNGZjY2Q0ZmEiLCJzdWIiOiJzeXN0ZW06c2VydmljZWFjY291bnQ6a3ViZXJuZXRlcy1kYXNoYm9hcmQ6YWRtaW4tdXNlciJ9.dIUpYhx0G8GvC26GQsHGr7wvWu0THntLHWGf1P-Ep7nWSeIBkM-QLtUxmOv3q1zz45xIyhTAuquZegQ1OH6kgD6UvPdf2GdfO6LbFU_yAWuMtYWTSgDwIbrP7L1yOBPwdrQFN1xjjHR6luc92g50vVdAetGEwXU5MN-dkEv-3Vu6bLJi9FbUWCdKw-I9kVqCka01acy6dJQdyvrI8Wr0y8tTA0gI3LxjAsS_WpUmgskJIsF2aKDmCvBA_Sh8bZfHmLEuFSRnOFbjFyH9w_tx8Ia7gqnMzrr3c43SvtNX99BfwRiVGpZ1UpKmPRwBAmnj53j2TrKT1vNQyD58btXlfwAccess the Kubernetes Dashboard using the URL https://192.168.50.11:30002/#/login using the token printed before:
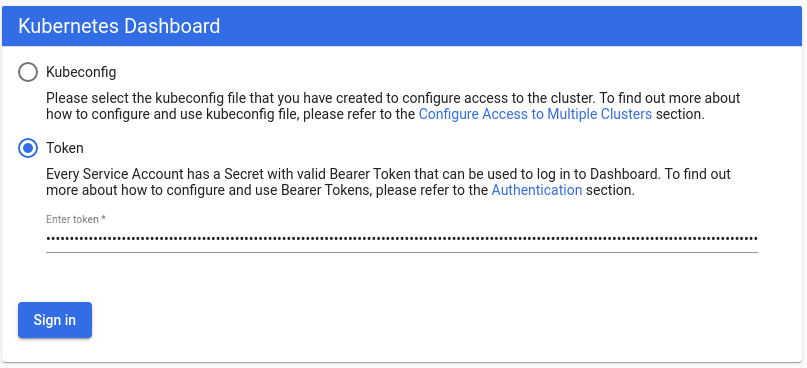
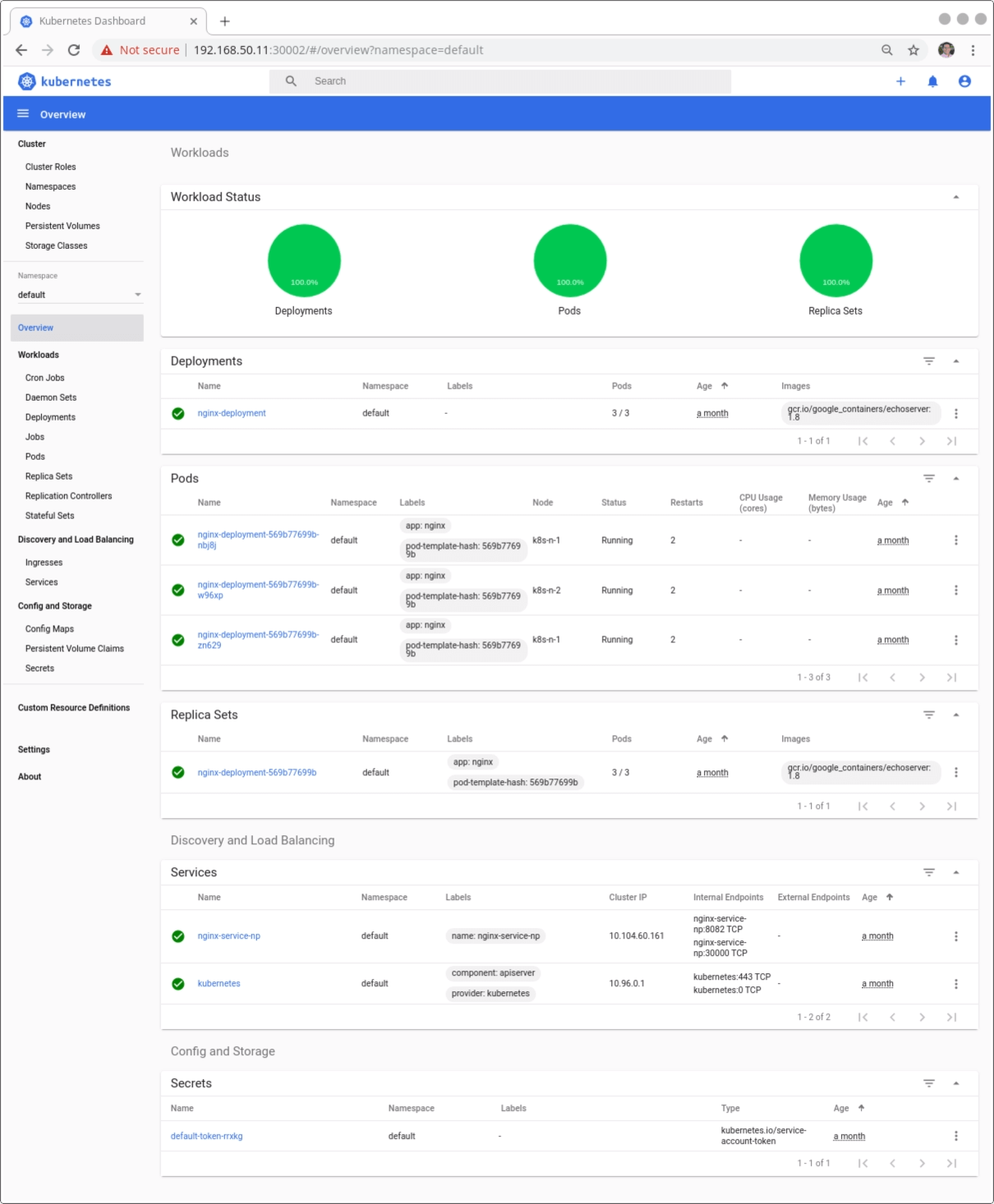
Please read other ways to publish the Kubernetes Dashboard on the Kubernetes Dashboard documentation.
#Create the cluster or start the cluster after a host reboot vagrant up #Execute again the Ansible playlist in all the vagrant boxes, useful during development of Ansible playbooks vagrant provision #Execute again the Ansible playlist in the Kubernetes node 1 vagrant provision k8s-n-1 #Poweroff the Kubernetes Cluster vagrant halt #Open an ssh connection to the Kubernetes master vagrant ssh k8s-m-1 #Open an ssh connection to the Kubernetes node 1 vagrant ssh k8s-n-1 #Open an ssh connection to the Kubernetes node 2 vagrant ssh k8s-n-2 #Stop all Vagrant machines (use vagrant up to start) vagrant halt
After installing Kubernetes using Vagrant:

IT Wonder Lab tutorials are based on the diverse experience of Javier Ruiz, who founded and bootstrapped a SaaS company in the energy sector. His company, later acquired by a NASDAQ traded company, managed over €2 billion per year of electricity for prominent energy producers across Europe and America. Javier has over 25 years of experience in building and managing IT companies, developing cloud infrastructure, leading cross-functional teams, and transitioning his own company from on-premises, consulting, and custom software development to a successful SaaS model that scaled globally.
For the "Access the Kubernetes Dashboard using the URL https://192.168.50.11:30002/#/login "
The Kubernetes dashboard pod is running on master node, that's why you used 192.168.50.11
If the pod was running on one of the worker nodes, then you would have to use the worker node IP.
I was banging my head as to why the URL was not working 😀
Then found out this info in kubernetes docs.